general chemistry laboratory manual
Summary
Discover the ultimate general chemistry lab manual, packed with experiments, safety tips, and practical insights. Perfect for students and professionals alike!

Welcome to the General Chemistry Laboratory Manual, your guide to mastering essential lab skills and safety protocols. This manual provides clear procedures, safety guidelines, and best practices for conducting experiments effectively and responsibly.
1;1 Purpose and Scope of the Manual
The General Chemistry Laboratory Manual serves as a comprehensive guide for students enrolled in general chemistry laboratory courses. Its primary purpose is to ensure safety, foster technical skills, and promote clear scientific communication through detailed procedures and best practices.

The manual is designed to align with course objectives, providing resources for understanding fundamental principles and conducting experiments responsibly. It emphasizes environmental compliance and proper chemical handling, making it an essential tool for both students and instructors.
1.2 Key Features and Benefits
This manual offers step-by-step experiment guides, safety protocols, and data analysis techniques; It enhances practical skills and ensures accurate record-keeping through detailed notebook sections. Additional resources include troubleshooting tips and visual aids to support learning. These features make it indispensable for achieving lab success and fostering a deeper understanding of chemistry concepts.
Laboratory Safety Guidelines
Adhere to safety rules, wear PPE, and follow proper chemical handling and disposal procedures. Familiarize yourself with emergency protocols and equipment to ensure a secure lab environment. Always prioritize safety.
2.1 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Wearing proper PPE is essential in the lab. This includes lab coats, safety goggles, gloves, and closed-toe shoes. PPE protects against chemical splashes, spills, and hazardous materials. Ensure all items are worn correctly and maintained in good condition. Familiarize yourself with PPE requirements for specific experiments. Proper use of PPE is crucial for personal safety and preventing accidents.
2.2 Emergency Procedures and Protocols
Know emergency procedures to handle accidents promptly. Familiarize yourself with fire extinguishers, eyewash stations, and emergency exits. In case of spills, contain them and alert staff. For injuries, provide first aid and seek medical help. Evacuate the lab during alarms and follow evacuation routes. Regular drills ensure preparedness for unexpected situations, ensuring safety for all laboratory personnel.
2.3 Safe Handling and Disposal of Chemicals
Handle chemicals with care, using appropriate PPE. Read SDS for specific hazards and precautions. Dispose of chemicals according to lab guidelines, segregating waste by type. Avoid mixing chemicals during disposal to prevent reactions. Contain spills immediately and clean them up safely. Consult lab staff for proper disposal methods and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
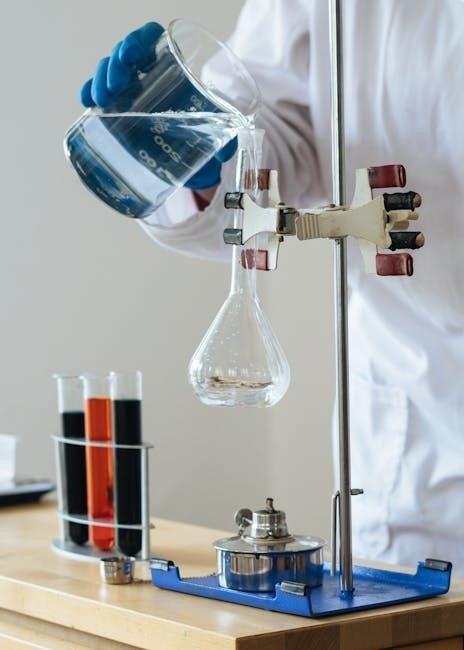

Essential Laboratory Equipment
Familiarize yourself with common glassware, instruments, and measurement tools. Burettes, pipettes, and balances are fundamental for precise experiments. Advanced equipment like spectrophotometers and chromatographs enhance data collection and analysis.
3.1 Common Laboratory Glassware and Instruments
Common laboratory glassware includes beakers, flasks, and test tubes for containing and measuring substances. Instruments like Bunsen burners, crucible tongs, and fume hoods are essential for heating, handling, and ventilation. These tools ensure accurate measurements, safe handling, and efficient experimentation in a chemistry lab setting.
3.2 Measurement Tools: Burettes, Pipettes, and Balances
Burettes measure precise liquid volumes, while pipettes ensure accurate transfer of specific amounts. Balances are used for weighing solids, providing essential data for stoichiometric calculations. These tools are crucial for maintaining precision and accuracy in laboratory experiments, enabling reliable quantitative analysis and experimental reproducibility.
3.3 Advanced Equipment: Spectrophotometers and Chromatographs
Spectrophotometers measure light absorption to analyze chemical concentrations and molecular structures. Chromatographs separate and identify compounds in mixtures, enabling precise qualitative and quantitative analysis. These advanced tools are essential for modern chemical research, offering high precision and versatility in experiments involving complex molecular interactions and synthesis.
Fundamental Laboratory Techniques
Mastering basic lab techniques like measuring, mixing, and heating is crucial for accurate experiments. These skills form the foundation for more complex procedures in chemistry.
4.1 Basic Techniques: Measuring, Mixing, and Heating
Accurate measuring, precise mixing, and controlled heating are foundational skills in chemistry. Use glassware like burettes and pipettes for precise measurements. Mixing involves combining substances thoroughly while minimizing waste. Heating techniques, such as using Bunsen burners, require attention to safety and temperature control to ensure reactions proceed as expected. These skills are essential for reliable experimental outcomes.
4.2 Advanced Techniques: Titration, Distillation, and Chromatography

Titration involves precise measurement of reactants to determine concentrations. Distillation separates substances based on boiling points, ensuring purity. Chromatography isolates components of a mixture for analysis. These advanced techniques are crucial for quantitative analysis, purification, and characterization of chemical substances, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in experimental workflows.
The Laboratory Notebook
The laboratory notebook is a critical record of scientific procedures, observations, and data. It is evaluated for neatness, completeness, and accuracy. Failure to maintain it properly may result in penalties.
5.1 Maintaining a Proper Laboratory Notebook
A well-maintained laboratory notebook is essential for accurate record-keeping. Include the date, title, and purpose of each experiment. Record observations, data, and calculations clearly. Use bullet points or numbered lists for organization. Ensure all entries are legible and dated. Notebooks are periodically reviewed for neatness, completeness, and accuracy. Failure to maintain proper records may result in penalties.
5.2 Writing Clear and Concise Laboratory Reports
Lab reports should be structured, clear, and concise. Include the purpose, procedure, data, results, and conclusions. Use proper scientific terminology and ensure clarity. Avoid unnecessary details and maintain professionalism. Proofread for errors. Reports are graded on accuracy, organization, and adherence to guidelines. Ensure all data is presented logically, and conclusions are supported by results.
5.3 Data Analysis and Interpretation
Data analysis involves accurately interpreting experimental results, identifying trends, and drawing meaningful conclusions. Use statistical methods to ensure precision and validate findings. Compare results with theoretical expectations and discuss any discrepancies. Present data clearly using tables, graphs, and charts. Interpretation should be logical, concise, and aligned with the experiment’s objectives, providing a clear understanding of the outcomes.

Common Experiments and Exercises
Common experiments include distillation, solubility determination, and stoichiometry. These exercises introduce fundamental concepts, enhancing practical skills and reinforcing theoretical knowledge through hands-on activities aligned with learning objectives.
6.1 Introductory Experiments: Familiarization with Lab Equipment

Introductory experiments focus on familiarizing students with lab equipment, such as glassware, burettes, and balances. These exercises help develop essential skills in measurement, mixing, and heating, ensuring a solid foundation for more complex procedures. Students learn to use fume hoods, pipettes, and other tools safely, preparing them for advanced experiments and fostering confidence in laboratory settings.
6.2 Quantitative Analysis: Stoichiometry and Mole Concepts
Experiments in this section focus on applying stoichiometric principles and mole concepts to solve quantitative chemistry problems. Students perform calculations to determine empirical formulas, limiting reactants, and theoretical yields. Practical exercises include titration, gravimetric analysis, and gas law applications, enhancing problem-solving skills and understanding of chemical reactions and their quantitative aspects.
6.3 Advanced Experiments: Chemical Synthesis and Characterization
This section involves complex experiments focusing on chemical synthesis, purification, and characterization. Students explore techniques like recrystallization, distillation, and chromatography to prepare and analyze compounds. Experiments include synthesizing coordination compounds, determining chemical properties, and using spectroscopic methods for molecular identification. These exercises enhance understanding of chemical reactions, purification processes, and material characterization in a practical setting.
Assessment and Evaluation
Laboratory performance is evaluated through quizzes, lab reports, and periodic notebook reviews. Grades are based on accuracy, completeness, and adherence to safety protocols and proper techniques.
7.1 Grading Criteria for Laboratory Work
Laboratory grades are determined by accuracy of data, completeness of reports, adherence to safety protocols, and proper laboratory techniques. Neatness, attention to detail, and timeliness of submissions are also considered. Quizzes assess understanding of procedures, while lab reports evaluate critical thinking and data interpretation skills, ensuring comprehensive evaluation of student performance.
7.2 Lab Reports and Quizzes

Lab reports and quizzes are integral to assessing student understanding. Reports must include objectives, procedures, data analysis, and conclusions, showcasing clarity and accuracy. Quizzes evaluate theoretical knowledge and practical application, ensuring students grasp key concepts and laboratory techniques effectively; Timely submissions and proper formatting are essential for full credit.
7.3 Final Assessments and Competency Checks
Final assessments evaluate comprehensive understanding of laboratory principles and techniques. Students must complete a practical exam, demonstrating accurate data collection and analysis. Competency checks ensure mastery of safety protocols, equipment operation, and experimental design. Grading emphasizes accuracy, critical thinking, and adherence to scientific methodologies. A minimum score of 50% is required to pass the competency evaluation.
Environmental and Safety Compliance
Adhering to environmental regulations and safety standards is crucial in the chemistry lab. This section emphasizes waste minimization, proper chemical disposal, and compliance with laboratory safety protocols to ensure a sustainable and safe working environment.
8.1 Waste Minimization and Management
Effective waste management involves minimizing chemical use and proper disposal of hazardous materials. Obtain only the required amount of chemicals for experiments and follow proper disposal methods. Segregate waste into designated containers to ensure environmental protection and compliance with safety regulations.
8.2 Compliance with Laboratory Regulations
Adherence to laboratory regulations is crucial for ensuring safety and environmental protection. Familiarize yourself with local and institutional guidelines, such as proper chemical handling and disposal. Regular training and updates on safety protocols are essential to maintain compliance and minimize risks in the laboratory environment.

Resources and References
Key resources include textbooks like Laboratory Manual for Principles of General Chemistry and online materials from universities. Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and laboratory guides are essential for safe practices and procedure details.
9.1 Recommended Textbooks and Online Materials
Essential textbooks include Laboratory Manual for Principles of General Chemistry by J.A. Beran and General Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach. Online resources like university lab manuals and educational websites provide additional support. Utilize these materials for in-depth understanding of lab procedures, safety protocols, and theoretical concepts.
9.2 Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and Laboratory Guides

Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are crucial for handling chemicals safely, detailing hazards, first aid, and disposal methods. The stockroom provides access to these sheets, ensuring safe practices and compliance with regulations. Always consult SDS before working with any chemical to prevent accidents and ensure proper handling.
The General Chemistry Laboratory Manual equips students with foundational skills and knowledge, fostering scientific inquiry and practical application in future academic and professional endeavors.
10.1 Summary of Key Takeaways
This manual emphasizes laboratory safety, proper equipment usage, and accurate data recording. It reinforces theoretical concepts through practical experiments, fostering analytical thinking and problem-solving skills essential for success in chemistry. By adhering to guidelines and maintaining a detailed notebook, students ensure precise and reliable results, preparing them for advanced scientific studies and real-world applications.
10.2 Encouragement for Continuous Learning
Continuous learning is key to excelling in chemistry. Use this manual as a foundation to explore advanced topics and refine your skills. Stay curious, engage with new challenges, and apply theoretical knowledge to real-world problems. Embrace lifelong learning to grow as a scientist and contribute meaningfully to the field of chemistry.